The forces that act on a building include long-term loads such as the building itself and furniture as well as short-term loads such as earthquakes, wind pressure, and accumulations of snow. The ability to resist these forces is referred to as “structural resistance.”
The strength of structural materials and joints is important for loads that are imposed from above. In addition, it is necessary that floors, bearing walls, and other elements have sufficient rigidity to counter horizontal forces. Toughness (tenacity) and yield strength of the structure (residence) as a whole to disperse and dissipate force are necessary for earthquake resistance.
For prefab housing, structural calculation methods are used and testing is performed according to the construction methods and structure to repeatedly confirm safety with respect to these various forces.
The Performance Indication System specifies the seven items shown in the table as performance indicators relating to structural safety. With regard to earthquake resistance, rank 1 is the level that satisfies the conditions specified in the Building Standards Act, and rank 3 can withstand 1.5 times the load, while rank 2 is an interim level between ranks 1 and 3.
| Item | Details | Ranks |
|---|---|---|
| Earthquake resistance rank (collapse prevention) | Resistance to collapse or destruction of the structural frame due to earthquake | 3・2・1 |
| Earthquake resistance rank (damage prevention) | Resistance to damage to the structural frame due to earthquake | 3・2・1 |
| Other earthquake proofing measures | Earthquake-proofing measures through seismic isolation | - |
| Wind resistance rank | Resistance to collapse or destruction of the structural frame and resistance to damage due to strong wind | 2・1 |
| Snow resistance rank | Resistance to collapse or destruction of the structural frame and resistance to damage due to the accumulation of snow on the roof | 2・1 |
| Allowable bearing capacity rank of the ground or piles, etc. and method of setting | Degree of force that can be withstood from the expected continuous load on the ground or piles and method that is the basis for setting that resistance force | - |
| Foundation structural method and type | Construction method and type of direct foundation or pile type, diameter, and length of pile foundation | - |
The meaning of wind resistance rank and snow resistance rank for rank 1 is that there is no damage under the conditions specified in the Building Standards Act and the structure will not collapse or be destroyed even if stronger forces are applied; for rank 2, no damage, collapse, or destruction even if external forces greater than those anticipated in the Building Standards Act are applied is required. Of Prefab housing that uses the Performance Indication System, close to 90% has received level 3, the highest level, for collapse and destruction resistance with respect to the earthquake resistance rank, indicating that these homes provide excellent earthquake resistance performance.
In addition, for the allowable foundation bearing capacity and the method of setting that capacity, the foundation construction method and type are not rank indicators; rather, the values and methods are indicated.
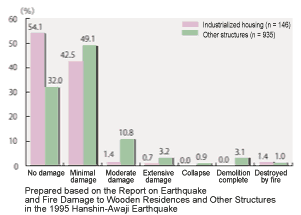
The Hanshin-Awaji Earthquake on January 17, 1995 resulted in extensive destruction including damage to more than 390,000 residences, of which 100,000 were completely destroyed.
A survey of all Association members revealed that a total of 107,723 prefab residential structures had been supplied in the regions designated under the Disaster Relief Act, and there were zero incidents of complete destruction or substantial damage, and only about 10% of the total incurred minor damage requiring repair including damage from foundation shifting and damage from destruction of nearby structures
Based on various survey data from the earthquake, tests were conducted on actual large-scale structures and other measures were implemented to develop technologies that can provide even greater earthquake resistance.

No matter how strong the structural frame and foundation, if the ground is ignored, it will not be a strong structure. Selecting a foundation type that is appropriate for the ground quality is the first step of earthquake-proof design.
In the case of prefab housing, before construction starts, an environmental survey, historical survey, and other research regarding the customer’s site are conducted and Swedish sounding and other tests are performed to thoroughly investigate the ground and create an optimal foundation for each site.
Earthquake-proofing measures through seismic isolation of structures was added to the Housing Quality Assurance Act as performance indicator items relating to structural stability in April 2007. Efforts have long been made to develop and supply prefab housing with high earthquake resistance by adopting seismic isolation and seismic control equipment. In the case of detached housing, relatively few units have been supplied because of cost restrictions, but efforts will be made to supply housing with seismic isolation and control measures through further technology development and cost reductions.

Full-scale vibration test
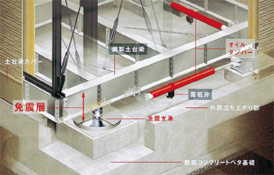
An example of a seismic isolation device
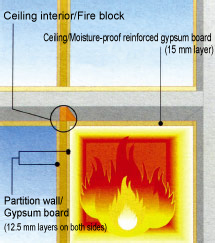
Generally, when a wooden house burns, temperatures can reach 1200°C. At that time, neighboring houses three meters away are subjected to a temperature of 830°C. To prevent the spread of fire, it is necessary that exterior rules be able to withstand maximum temperatures of 830°C if a neighboring house is on fire and also that the temperature of the other side of exterior walls does not exceed 260°C, the ignition point of wooden materials.
Under the Performance Indication System, exterior walls and other areas that are susceptible to catching fire under these temperature conditions (first-story exterior walls whose center is within three meters from the property line or center of the street and second-story and higher exterior walls whose center is within three meters) are classified from rank 1 to rank 4 according to how long they can withstand these temperatures.
| Item | Details | Rank |
|---|---|---|
| Fire resistance rank (Areas susceptible to catching fire (excluding openings) |
Able to block heat for 60 minutes or more | Rank4 |
| Able to block heat for 45 minutes or more | Rank3 | |
| Able to block heat for 20 minutes or more | Rank2 | |
| Other | Rank1 |
Prefab housing uses a variety of materials for exterior walls depending on the structure and construction methods, but internal and public testing agency fire resistance tests are conducted and ongoing efforts are made to satisfy the strict standards and ensure outstanding fire resistance performance.

Fire test on an actual house

Fireproofing test furnace for walls

Exterior wall fire resistance (illustrative)
When a fire breaks out, the flames from curtains, carpeting, and so on that have caught fire initially spread gradually, and the fire is limited to just one portion of the interior. When the flames reach the ceiling, combustible gases fill the interior, and when those gases reach a certain temperature and concentration, the fire can suddenly spread like an explosion. This is referred to as flashover.
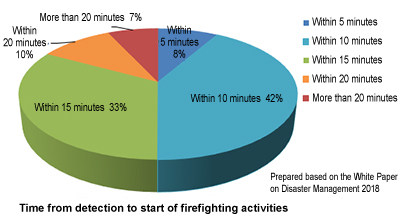
According to statistics, fire trucks arrive at the scene of a fire and begin firefighting activities within 15 minutes after receiving a report in 83% of cases. In order to minimize the extent of the fire damage, it is important to make the home interior incombustible and prevent the initial spread of fire so that flashover does not occur.
In prefab housing, gypsum board is used for interior walls and the interior side of ceilings, and depending on the structure, fire stop materials may be placed inside walls and other measures may be implemented as means of curtailing the spread of fire.
Under the Performance Indication System, openings of areas that are susceptible to catching fire are also evaluation items. Rank 1 openings use conventional aluminum windows and so on. Rank two requires fire-prevention windows that include wired glass and so on or installation of steel or stainless steel shutters or rain shutters.
Rank 3 is a specification level that is rarely required in general detached homes.In addition to enhancing the fire resistance of openings, consideration is also given to various aspects in plans such as installing balconies above openings that have the effect of preventing the spread of fire to upper floors.
| Item | Details | Rank |
|---|---|---|
| Fire resistance rank (Areas susceptible to catching fire (openings) |
Able to block heat for 60 minutes or more | Rank3 |
| Able to block heat for 20 minutes or more | Rank2 | |
| Other | Rank1 |
Many people who are injured by fire are elderly, sick, or disabled, and the late night stands out as a time when harm is more likely to increase. Delayed escape from fire is the primary cause.
In response to this, amendments to the Fire Service Act made installation of fire detectors and alarms in all bedrooms as well as on all floors and in hallways that contain bedrooms mandatory in new residential construction as of June 2006.
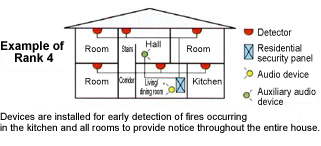
The Performance Indication System establishes ranks for fire detectors and alarms to support the early detection of fire.
Evaluation is conducted based on four ranks from rank 1 to rank 4 according to the installation locations and number of sensors that operate by detecting heat or smoke. Rank 4 requires that detectors be installed in all kitchens and bedrooms as well as on all floors and in all hallways and further that alarms can be conveyed to all portions of the structure.
Early detection as well as ensuring an escape route or both important. The Performance Indication System evaluates whether balconies and evacuation equipment such as escape ladders that lead directly to direct stairs are installed as escape measures for three-story buildings.
In prefab housing, even in emergencies when a normal walking route cannot be secured, fire detectors and evacuation equipment are installed to conform with rank 4, the highest rank, so that occupants can safely escape.
Japan has a lot of rain throughout the year and humidity is high. These climate conditions can lead to rotting of the foundations and pillars of wooden houses and rust can occur in the structural members of steel-framed housing, reducing strength and durability.
Deterioration of wooden materials due to rotting and deterioration of the strength of steel frames due to rust is said to have been the cause of collapse of many houses in the Hanshin-Awaji Earthquake,
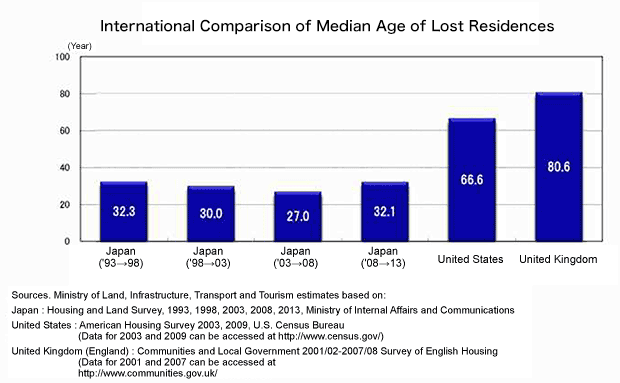
In addition, the lifespan of Japanese houses is extremely short compared to that of houses in Europe and the United States. This is not a matter of physical durability, but is said to be the result of changes in living standards (average total floor area) and lifestyles, and consequently, even if these problems are solved in the future, further enhancements in the physical durability of structural frames will be needed to achieve housing lifespans comparable to those in the West.
Various technologies are being developed to enhance the durability of structural frames and other components so that two and even three generations can live in prefab housing.
One of the key characteristics of the durability of prefab housing is that preservative treatment of wood materials and rust proofing treatment of steel materials are performed in a factory. This means that joints and other areas for which on-site durability treatment is difficult can be fully treated. These items are rigorously checked under the plant quality control standards of each company and achieve high levels of durability that can be maintain performance over many years.
The Performance Indication System specifies deterioration countermeasure ranks in the form of the degree of countermeasures necessary to extend the time until large-scale repairs will be necessary such as replacing materials used in the structural frame and so on. Of prefab housing that uses the Performance Indication System, the percentage that achieves rank 3, the highest rank, indicating countermeasures that can extend the lifespan of the structure frame to three generations (75 to 90 years), is high at 95.5%.
| Item | Details | Rank |
|---|---|---|
| Deterioration countermeasures rank (structural frame) |
Measures to extend the period until major repairs are needed to 75 to 90 years under normally-expected natural conditions | Rank3 |
| Measures to extend the period until major repairs are needed to 50 to 60 years under the same conditions as rank 3 | Rank2 | |
| Measures specified by the Building Standards Act | Rank1 |
The red rust that occurs on steel materials is the result of the oxidation of iron. Oxidation of iron is a phenomenon linked to oxygen in water and the air, and if left unaddressed, the corrosion can spread to the interior of the material. To prevent this, iron and steel prefab housing employs anti-rust treatment whereby electro-galvanizing is performed or anti-rust paint is applied to the surface of iron and steel materials through or electrodeposition at the factory.
The causes of wood decay include decay due to fungi and feeding damage caused by termites. Both spread when the temperature and humidity conditions are suitable, and therefore, the first step is moisture proofing measures. For wooden prefab housing, the water content of wood materials is strictly managed, and wood preservation and termicide agents are applied to the necessary wood materials by coating, dipping, pressure injection, or other methods during the factory production phase.
Even sturdy steel-frame concrete structures lose structural durability when rust occurs in rebar and cracks occurs in concrete. Because of rebar rest is neutralization of the concrete. When the concrete is poured, it is alkaline, and this plays the role of preventing rusting of the rebar that is embedded in the concrete. As the concrete reacts with acidic gases in the air and neutralizes, this rust prevention effect is lost. For concrete prefab housing, the concrete mix is rigorously designed and managed to achieve high-quality concrete that delays neutralization and does not include harmful substances.
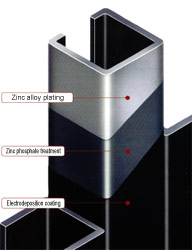
Anti-rust treatment of steel frame members
A three-layer anti-rust treatment is performed using advanced anti-rust technologies
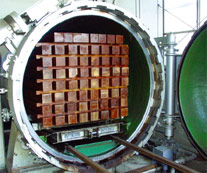
Wood preservation treatment
Pressure injection treatment is used to ensure that the chemicals adequately penetrate the wood

Concrete accelerated durability testing
The purple area indicates where alkalinity has been maintained and neutralization has not progressed.
Buildings are made from the combination of the structural frame, which has a relatively long lifespan, and pipes, interior and exterior materials, and so on, which have shorter life spans.
Measures that facilitate maintenance and management of those areas with shorter useful lives including day-to-day inspection and repairs are important.
The Performance Indication System specifies ranks for maintenance and management measures with respect to day-to-day maintenance and management of water supply and drain pipes and gas pipes. Of prefab housing that use the Performance Indication System, 99% achieves rank 3.
| Item | Details | Rank |
|---|---|---|
| Maintenance and management measures rank (dedicated pipes) |
Pipe maintenance and management can be performed without harming the structural frame or finish materials | Rank3 |
| Pipe maintenance and management can be performed without harming the structural frame | Rank2 | |
| Other | Rank1 |
In addition, in apartment buildings, consideration is given to the placement of shared drain pipes to facilitate replacement.
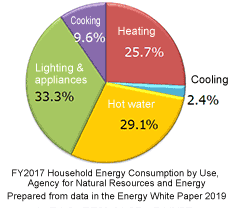
Japan depends on imports for the majority of its fossil fuels, which are the primary energy sources, and ensuring stable energy supplies is a crucial issue. In light of the coming into effect of the Paris Agreement, an international framework for reducing greenhouse gas emissions, a medium-term target has been set in the Global Warming Countermeasures Plan to reduce greenhouse gas emissions in FY 2030 by 26.0% compared to FY2013.
Under these circumstances, the amount of energy consumed by homes and buildings categorized in the residential and commercial category must be reduced by about 20% compared to FY2013, making enhancing the energy-saving performance of homes and buildings a pressing issue.

Energy-saving standards were first established in 1980 under the Act on the Rational Use of Energy. Later, the required standards were revised and made stricter in accordance with the times under the new energy-saving standards in 1992 and next-generation energy-saving standards in 1999.
The energy-saving standards were again revised in 2013. Previously, the standards addressed only the heat insulation performance of the exterior skin of a structure, but under the 2013 standards, evaluation of the overall energy-saving performance measured according to primary energy consumption including equipment used in the home was added. Until then, insulating a building contributed enhancing comfort and saving energy used on heating and air conditioning, but measures that address the performance of heating and air conditioning performance, water heaters used in kitchens and baths, lighting, and so on are closely related to reducing energy consumption, and therefore, they were added to the energy-saving standards.
In July 2015, a new law on energy-saving in homes and buildings, the Act on the Improvement of Energy Consumption Performance of Homes and Buildings, was enacted. Guidance measures come into effect in April 2016, and regulatory measures came into effect in April 2017. In addition, the Act was revised in May 2019.
Prefab housing continuously adapts to the changes in the times including these new energy-saving standards, and efforts are being made to promote energy-saving homes by improving insulation performance and introducing the latest high-efficiency and energy-generating equipment. Energy-saving residences are intended not just to reduce energy consumption, but also to enable comfortable living during the cold of winter and the heat of summer.
Of prefab housing that uses the Performance Indication System, the percentage of detached homes that achieve rank 4 (equivalent to rank 4 insulation performance and the 2016 building energy-saving standards), the highest rank for comfortable living, is high at 99%.
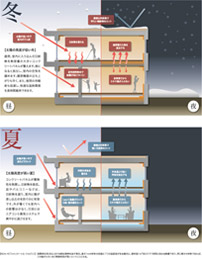
Example of high insulation performance and high airtightness

Example of wall insulation
In addition to residential equipment such as highly-energy efficient water heaters, heating and air conditioning equipment, and lighting, prefab housing actively adopts solar power generation systems that create energy and battery systems that store energy, and we are promoting housing with outstanding energy-saving performance. We are also promoting the use of energy optimization through the introduction of home energy management systems (HEMS) that network this equipment, automatically controls devices, and makes energy consumption visible.
These energy-saving homes can also satisfy the low-carbon building standards by using wood materials, implementing water-saving measures, and taking heat island countermeasures as CO2 reduction measures. The low-carbon building standards are approximately 10% stricter than the energy-saving standards in terms of primary energy consumption and also include low-carbon measures. Prefab housing can comply with rank 5, the highest rank for primary energy consumption equivalent to the low-carbon building standards, under these low-carbon buildings standards and the Performance Indication System.

Examples of lithium-ion batteries

Examples of a home energy management system (HEMS)
The government’s Strategic Energy Plan provides that “with regard to housing, efforts shall be made to achieve net zero energy houses (ZEH) for standard new construction by 2020 and for average new construction by 2030.”
Under its Eco Action 2020 plan, the Japan Prefabricated Construction Suppliers and Manufacturers Association will promote the development and supply of new construction ZEH and has set a new construction ZEH supply ratio target of 70% and a target of reducing CO2 emissions during the residential stage per unit by 60% compared to 2010.
ZEH means housing that seeks to achieve zero net annual primary energy consumption through enhanced insulation performance, the introduction of high-performance equipment, and other measures.


Figures: Examples of ZEH and other energy-saving homes
The living standard (average floor area) of homeowners steadily increased during the period of rapid economic growth starting in the mid-1950s until the early 1990s. The floor area of prefab housing in particular has exceeded 140㎡ since 1994, and currently is flat or decreasing slightly, but even so, this is substantially larger than the national general residence floor area guidance of 125㎡ (four-person household) and the national average.
It is necessary to provide sufficient space so that residents can remain in their homes for extended periods while adapting to diverse lifestyles. Prefab housing offers various options that provide ample space tailored to the customer’s site conditions and family structure.

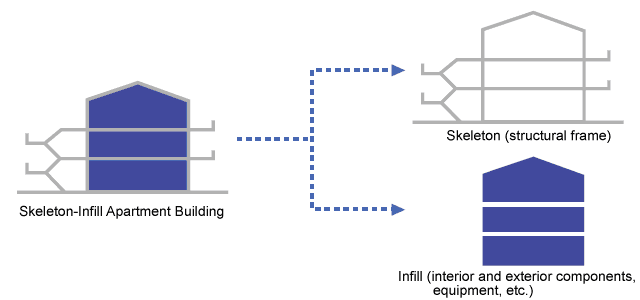
The second condition necessary to adapt to changes in lifestyle or life stage is ease of reconstruction or renovation. Recently, “SI housing” has been proposed at housing that has this characteristic. SI housing is divided into the structural frame (skeleton) and the interior and exterior components, equipment, and so on (infill). Under this system of housing, the skeleton is made strong to enable use for as long as possible, and the infill can be freely changed to the greatest extent possible. This concept was first to generally adopted with reinforced concrete apartment buildings. In the case of detached housing, the skeleton and infill are not completely separated for housing proposals, but many proposals have been made for “versatile housing” where the living space surrounded by a structural frame is made as large as possible based on excellent structural durability, and the floor plan can be changed by removing elements when necessary.
Active efforts are being made regarding prefabricated housing to develop SI homes by improving physical durability further and developing components that are easy to replace.